Organisational Structure and Different Types of Structures
Organizational structure and different types of structures
Organizational structure is the internal, formal framework of a business that shows the way in which management is linked together and how the authority is transmitted. (Stimpson P. 2011) It is basically a framework used to describe the hierarchy in an organization. Every business needs to have its own organizational structure as it helps in identifying the job at each level of an individual followed by its functions and it also assists in obtaining their own goals for development. There is a need for every type of organization to have its own structure especially when it comes to large enterprises as it becomes difficult activities for the various departments and functions. Following are the various type of organization structure a business can have:
- Functional Structure:

Figure 1: Functional Source: businessmates.org,2014
This type of structure mainly focuses on the functions set up for each department of the organization. It works well for small enterprises as each department is mostly dependent on the knowledge, skill, and talent of the other employees to support themselves. It leads to specialization and efficiency in the performance, however on the other hand it can also lead to conflicts as it restricts the employee of different departments to communicate and coordinate with each other because of the boundaries of working in their own department separately.
- Product Structure:

Figure 2: Product Source: tutorialspoint.com,2014
Its focus is on the organization's product lines and this type of structure can mostly be found in retail stores that exist in a number of cities. Mostly large enterprises that have a different types of products with their own departments and functions have this structure. Despite this structure being faster when it comes to making decisions, it can also lead to extra costs due to repeated functions for each product.
- Regional Structure:

Figure 3: Regional Source: cnx.org,2014
Organizations that develop and duplicate departments in various functional areas across the region use this structure as they want to focus on the local strategies of the area to keep up with the competition by studying their preferences and demands.
- Multi-divisional Structure:

Figure 4: Multi-division Source: creately.com,2014
This structure is used for large companies that operate in wide geographical areas as the number of functions, employees and activities are very large. The benefit of this structure is that it is more specific and rapid but on the other hand due to the employees being in different divisions the communication is uneasy.
- Multi-function Structure:
It mostly focuses on achieving the business goals as it diverse functional expertise to work together on it.
- Matrix Structure:

Figure 5: Matrix Source: unc.edu,2014
This happens to be a combination of the divisional and functional structure as it handles product lines and functions together. Though it provides the benefit of both structures to be in one enterprise it can create a conflict when it comes to increased costs and internal complexity.
Organizational culture and different types of cultures
Culture is compromised of the assumptions, values, norms, and tangible signs of organization members and their behavior. Members of the organization soon come to sense the particular culture of an organization. (Katrin O.,2010) Organizational culture refers to the values, expectations, and behavior that hold the organization together. It basically based on customs, beliefs, and rules which develop over time. It also refers to an arrangement of the objectives and ideas made by the people in the organization and is not only referred to the people employed in the company but also their products, services, and the various process involved. There are four main types of cultures:
- Power Culture: This is used by most organizations where the power lies at the top level of management as they make the decisions. It is mostly suitable for organizations that have a small number of employees. The relationship is adaptive and informal which leads to good personal relations.
- Role Culture: This is mostly found in the large hierarchical enterprise where each employee has their own role to perform specifically. Here the employees work more closely to their job description and are creative in their own way. The relationship is formal in nature.
- Task Culture: Here teams are made to complete tasks appointed. Every team ends up making their own cultures as they have their own authority to make decisions. In this type of culture, teams are creative but on the other hand, it can also be costly due to the market price being demanded for their service by the experts.
- Person Culture: This is more of an individualistic culture where everyone is allowed to express themselves and make decisions of their own.
Compare and contrast two organizational charts of real companies
The two organizations taken for this report are Nestle and McDonalds.
Nestle

Figure 6: Nestle Logo Source: consumerbrands.com, 2014
Nestle is a multinational company headquartered in Switzerland. Its main focus is to provide health-oriented food for its customers for a healthier lifestyle following by different varieties of products including beverages. They have products which are specially for people who are very conscious about weight gain, cornflakes that contain iron and proteins for the development of young children. It believes in satisfying its customers at any point of the day and all around the world as its products can be found worldwide. They want to provide reliable quality food products which will contribute towards the nutritional factor of consumers until the brand's existence. (nestle.co.za, 2014)
Organizational Chart of Nestle
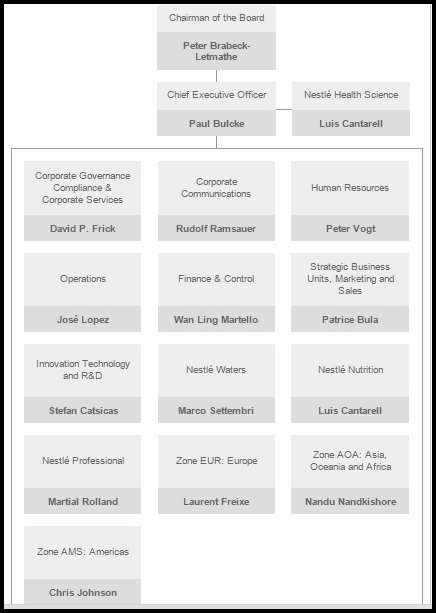
Figure 7: Nestle Organisational Chart Source: nestle.com,2014
It can clearly be seen from their organizational structure that Peter Brabeck-Letmathe is the main chairman of this multinational organization. According to their website there are 14 members of the Board of Directors. Here the shareholder are the owners of the company followed by them having their own separate legal identity from the main owner.
McDonalds

Figure 7: McDonald's Source: logos.wikia.com,2014
Mcdonalds has been operating since the year 1948 which is more than 100 years ago, they have a well- established market throughout the different countries in the world. McDonald's is the leading global foodservice retailer with more than 34,000 local restaurants serving nearly 69 million people in 119 countries each day.
Organizational Chart of McDonald's
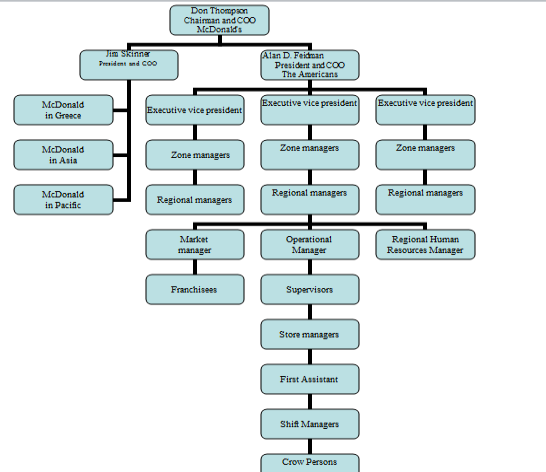
Figure 8: Organisation Chart McDonalds Source: (Webcache.googleusercontent.com, 2014)
Over 70% of Mcdonald's are run through franchises. It is a form of organization where a business that doesn't want to sell directly comes in contact with a franchisee to sell their product to consumers based on certain rules and regulations. McDonald's has a functional structure design. Big companies normally have this structure where the departments carry out most of the work. According to the chart above, you can see how everything is structured along the lines. Their hierarchy starts from their Chief Executive Officer who is at the top followed by the operating officer and so on. When it comes to comparing these two organizations they are both multinational companies with a reputed image among their customers. Both of their purpose of existence is to engage into getting maximum customer satisfaction as their Research and Development department is very efficient. On the contrary, Nestle happens to have a decentralized form of the structure where the authority makes the decision through all levels of the organization which means that their strategies and rules are flexible. Whereas Mcdonald's has a centralized structure where the top management makes the strategies and decisions that make the procedures and rules become rigid. Nestle has a structure in their hierarchy chart which is tall with a long chain of command. On the other hand, Mcdonald's has a flat structure with a controlling group at each level of their hierarchy. Followed by Nestle having a decentralized structure, it makes their rules and regulation flexible where the management have the opportunity to make changes in decision according to the situation. But in Mcdonald's due to a lack of flexibility in their organizational structure their effectiveness and efficiency lack behind in decision making. The major difference between these two companies is that Nestle has a regional structure which is based on different geographical areas. Whereas Mcdonald's has a functional structure in which different functions are performed by different departments.
Cite this page
Organisational Structure and Different Types of Structures. (2017, Jun 26).
Retrieved April 18, 2024 , from
https://studydriver.com/organisational-structure-and-different-types-of-structures/
Stuck on ideas? Struggling with a concept?
A professional writer will make a clear, mistake-free paper for you!
Get help with your assignmentLeave your email and we will send a sample to you.
Perfect!
Please check your inbox